Scientist have collaborated on the global warming trend and have observed since the 20th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect".this results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space.
Some gases in the atmosphere block heat from escaping. Long-living gases that remain semi-permanent in the atmosphere and do not respond physically or chemically to changes in temperature are described as "forcing" climate change. Gases, such as water vapor, which respond physically or chemically to changes in temperature are seen as "feedbacks."
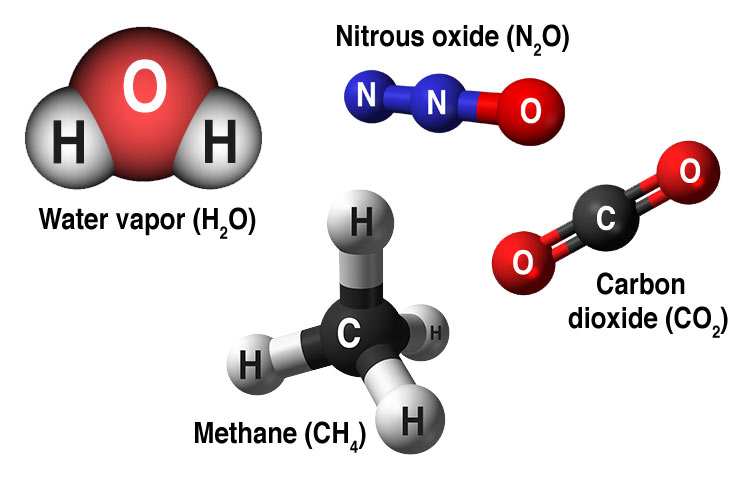
Gases that can contribute to the greenhouse effect include:
Water vapor. The most abundant greenhouse gas, but most important, it acts as a feedback to the climate. Water vapor increases as the Earth's atmosphere warms, but so does the possibility of clouds and precipitation, making these some of the most important feedback mechanisms of the greenhouse effect.
Carbon dioxide (CO2). A minor but a very important component of the atmosphere, carbon dioxide is released through natural processes such as respiration and volcano eruptions and through human activities such as deforestation, land use changes, and burning fossil fuels. Humans have increased the atmospheric CO2 concentration by more than a third since the Industrial Revolution began. This is the most important long-lived "forcing" of climate change.
Methane. A hydrocarbon gas produced both through natural sources and human activities, including the decomposition of wastes in landfills, agriculture, and especially rice cultivation, as well as ruminant digestion and manure management associated with the domestic livestock. On a molecule-for-molecule basis, methane is a far more active greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide, but also one which is much less abundant in the atmosphere.
On Earth, human activities are changing the natural greenhouse. Over the last century the burning of fossil fuels which includes- coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). This happens because the coal or oil burning process combines carbon with oxygen in the air to create CO2. To a lesser extent, the clearing of land for agriculture, industry, and other human activities have increased concentrations of greenhouse gases.

Not enough greenhouse effect: Mars has a very thin atmosphere, nearly all carbon dioxide. Because of the low atmospheric pressure, and little to no methane or water vapor to reinforce the weak greenhouse effect, Mars has a largely frozen surface that shows no evidence of life.

Too much greenhouse effect: The atmosphere of Venus, just like Mars, is nearly all carbon dioxide. But Venus has nearly 154,000 times as much carbon dioxide in its atmosphere as Earth (and about 19,000 times as much as Mars does), producing a runaway greenhouse effect and a surface temperature hot enough to melt lead.
The industrial activities that our modern civilization depends upon have raised atmospheric carbon dioxide levels from 280 parts per million to 400 parts per million in the last 150 years. The panels also stated that there's a better than 95 percent probability that human-produced greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide have caused much of the observed increase in Earth's temperatures over the past 50 years.
It's reasonable to assume that the changes in the Sun's energy output would cause the climate to change, since the Sun is the fundamental source of energy that drives our climate system.
Leave a comment